引言
大数据时代,类似sum求和或者avg平均值的操作还是相对容易,而比如类似算网站uv或者
找出网站访问最频繁访客会比较困难,es中提供了一种cardinality聚合来解决这类问题.
1 | curl -XGET "http://localhost:9200/_search" -d' |
基数估算算法
数据集小的时候,当然可以使用hashset,但是数据量过大的时候,内存使用就会很致命.传统的基数计数实现有两种,基于B树和基于bitmap,B树在问题在于不能高效合并,bitmap问题在于bitmap的长度与集合中元素个数无关,而是与基数的上限有关,例如“00100110”表示集合 {2,5,6}。bitmap中1的数量就是这个集合的基数,
这两种方法在大数据场景下都会有内存问题.
幸运的是,还有其他的基数计数算法.其中比较有名的就是linear counting和loglog counting,HyperLogLog
lc算法
LC的基本思路是:设有一哈希函数H,其哈希结果空间有m个值(最小值0,最大值m-1),并且哈希结果服从均匀分布。使用一个长度为m的bitmap,每个bit为一个桶,均初始化为0,设一个集合的基数为n,此集合所有元素通过H哈希到bitmap中,如果某一个元素被哈希到第k个比特并且第k个比特为0,则将其置为1。当集合所有元素哈希完成后,设bitmap中还有u个bit为0。则:
n^=−mlogumn^=−mlogum
为n的一个估计,且为最大似然估计(MLE)。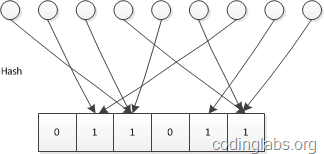
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8class LinearCounter {
BitSet mask = new BitSet(m) // m is a design parameter
void add(value) {
int position = hash(value) // map the value to the range 0..m
mask.set(position) // sets a bit in the mask to 1
}
}
精度要求越高,则bitmap的长度越大。随着m和n的增大,m大约为n的十分之一。因此LC所需要的空间只有传统的bitmap直接映射方法的1/10.
llc算法
LLC的空间复杂度仅有O(log2(log2(Nmax))),使得通过KB级内存估计数亿级别的基数成为可能.
例如,假设基数的上限为1亿,原始bitmap方法需要12.5M内存,而LogLog Counting只需不到1K内存(640字节)就可以在标准误差不超过4%的精度下对基数进行估计,因此目前在处理大数据的基数计算问题时,所采用算法基本为LLC或其几个变种1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17class LogLogCounter {
int H // H is a design parameter
int m = 2^k // k is a design parameter
etype[] estimators = new etype[m] // etype is a design parameter
void add(value) {
hashedValue = hash(value)
bucket = getBits(hashedValue, 0, k)
estimators[bucket] = max(
estimators[bucket],
rank( getBits(hashedValue, k, H) )
)
}
getBits(value, int start, int end)
rank(value)
}
小结
- 它们都是基于hash而非数值
- 它们返回的结果都是近似值
- linear counting作为一个早期的算法,空间复杂度并不优秀,在基数大的时候结果会很不准,很少单独使用
- 相比LC其最大的优势就是内存使用极少。不过LLC也有自己的问题,就是当n不是特别大时,其估计误差过大
- HyperLogLog是一种结合LC和LLC的一种改进算法,可以用相对固定的内存估算任意大集合的计数
es中主要参考了google出品的HyperLogLog++算法,略有改动,在一定条件下,lc算法会升级到hll算法,详见es源码中org.elasticsearch.search.aggregations.metrics.cardinality.HyperLogLogPlusPlus类.
精度和内存
为了节约内存,精度方面会有所牺牲.es提供了一个可配置的precision_threshold参数,来配置cardinality的精度,
threshold参数的取值范围在0-4w,默认为3000,
精度和内存的使用都与这个参数相关,假设precision_threshold为N,那么你期望每个分片每个聚合桶上的内存大约是8*N字节.
源码中可以发现,precision_threshold会转化成precision精度,precision的取值范围在4-18,默认为14,
也就是对应precision_threshold=30001
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11/**
* Compute the required precision so that <code>count</code> distinct entries
* would be counted with linear counting.
*/
public static int precisionFromThreshold(long count) {
final long hashTableEntries = (long) Math.ceil(count / MAX_LOAD_FACTOR);
int precision = PackedInts.bitsRequired(hashTableEntries * Integer.BYTES);
precision = Math.max(precision, MIN_PRECISION);
precision = Math.min(precision, MAX_PRECISION);
return precision;
}
下面是一个相对精度丢失图: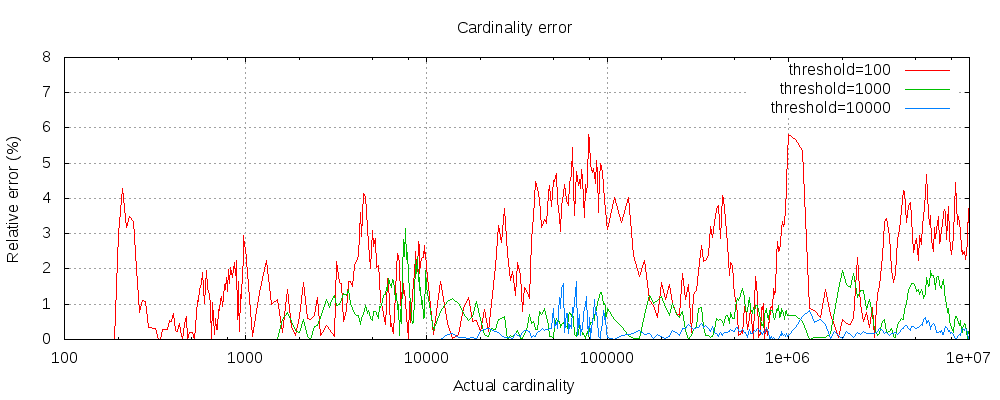
对于三种阈值,在不同基数下的精度丢失,可以发现就算阈值低至100,在百千万级别的数据量下.精度丢失也在5%以下